
- Local internet usage monitor mac os x#
- Local internet usage monitor mac os#
- Local internet usage monitor software#
It was originally measured in bit/s per second.
Local internet usage monitor software#
List of Best Software to Monitor Internet Usage on Windows 10, 11
Local internet usage monitor mac os#
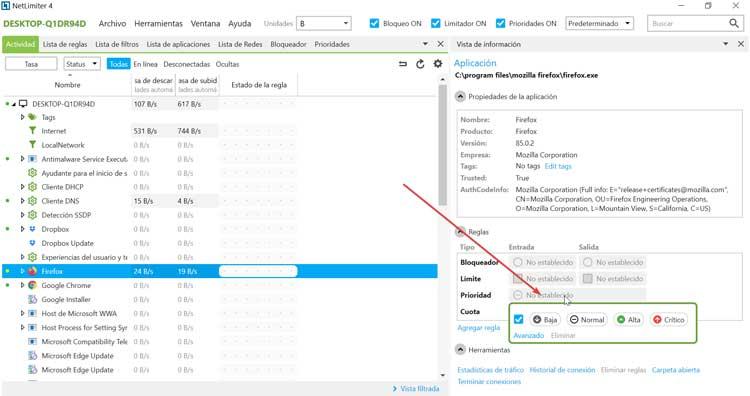
At least with Linux iptables you can, and I'm pretty sure BSD pf, and probably Mac OS X. You can probably create a firewall rule to count either of those.

Sometimes, for example, what appears to be a local machine on your Ethernet segment is actually over a VPN, over the Internet (this isn't crazy, it's very useful for when remote users need to use various Windows services). Requires in-depth knowledge of the network to figure if a destination is going to be local or not-and, with things like VPNs, that may vary over time.įinally, "Internet traffic" isn't the opposite of any of those. This is a reasonable meaning depending on how your network is set up (e.g., maybe you have fast fiber between your locations, but your Internet connections are much slower, or charged per-GB). You need network knowledge to distinguish local from non-local traffic with this definition.Īnother meaning would be "IP traffic destined to machines in my organization".
E.g., at my office we have several subnets in use, with routers between them, but traffic from one subnet to the other is still clearly local. This probably isn't want anyone means when they say "local traffic".Īnother meaning would be "IP traffic destined to machines in this (physical) location".
Local internet usage monitor mac os x#
The easiest way to count this is going to be either the routing table (if Mac OS X counts traffic stats per route, the routes on the various gateways will give you non-local traffic) or with a firewall rule. That'd be traffic that has a destination address inside the local subnet. The next easiest meaning would be "IP traffic destined to machines on the same subnet". This is one thing that people mean when they say local (and what I was thinking of when I answered). The easiest meaning of "local traffic" is traffic that does not leave the machine its generated on (two programs on the same machine talking to each other, for example). Answering you comment about which interfaces carry local traffic is actually complicated, because it depends on what you mean by local traffic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
